Inhaltsverzeichnis
Neuinstallation ioBroker auf einem R-Pi 3 B+ oder 4 B
Quellen:
Das Grundsystems
Installation
Die Verwendung von InfluxDB 2.x setzt ein 64-bit Betriebssystem voraus.
Ein Desktop bzw. eine vollständige grafische Oberfläche wird nicht benötigt. Daher bezeichnet man ein solches System als „Headless“. Somit basiert dieses Heimautomatisierungsprojekt auf einem Raspberry Pi OS (32 oder 64-bit) Lite.
# Raspberry Pi Image besorgen #wget https://downloads.raspberrypi.org/raspios_lite_armhf/images/raspios_lite_armhf-2023-02-22/2023-02-21-raspios-bullseye-armhf-lite.img.xz wget https://downloads.raspberrypi.com/raspios_lite_armhf/images/raspios_lite_armhf-2023-10-10/2023-10-10-raspios-bookworm-armhf-lite.img.xz oder #wget https://downloads.raspberrypi.org/raspios_lite_arm64/images/raspios_lite_arm64-2023-02-22/2023-02-21-raspios-bullseye-arm64-lite.img.xz wget https://downloads.raspberrypi.com/raspios_lite_arm64/images/raspios_lite_arm64-2023-10-10/2023-10-10-raspios-bookworm-arm64-lite.img.xz # R-Pi Imager herunterladen und intallieren: wget https://downloads.raspberrypi.org/imager/imager_latest_amd64.deb sudo dpkg -i imager_latest_amd64.deb rpi-imager #sudo touch /media/<benutzername>/bootfs/ssh #sync # SD-Karte aushängen und damit den R-Pi booten
Konfiguration
Während des Bootvorganges erhält der Raspberry eine IP Adresse vom Router. Diese kann über die entsprechende Weboberfläche des Routers ermittelt werden.
# Grundsystem auf den aktuellen Stand bringen: ssh -l pi <IP> sudo su apt-get update && sudo apt-get upgrade apt-get install aptitude mc apt-transport-https software-properties-common raspi-gpio raspi-config nonint do_hostname iobroker raspi-config nonint do_onewire 0 raspi-config nonint do_change_locale de_DE.UTF-8 UTF-8 raspi-config nonint do_expand_rootfs raspi-config nonint do_update reboot # Feste IP für eth0 einstellen: mcedit /etc/dhcpcd.conf interface eth0 static ip_address=192.168.10.11/24 static routers=192.168.10.1 static domain_name_servers=192.168.10.1 # # Seit OS "Bookworm": nmcli -p connection show nmcli con mod "Kabelgebundene Verbindung 1" ipv4.addresses 192.168.10.11/24 ipv4.method manual nmcli con mod "Kabelgebundene Verbindung 1" ipv4.gateway 192.168.10.1 nmcli con mod "Kabelgebundene Verbindung 1" ipv4.dns "192.168.10.1" reboot # oder nmcli c down "Kabelgebundene Verbindung 1" && sudo nmcli c up "Kabelgebundene Verbindung 1" # # nicht benötigte Dienste beenden und/oder entfernen: systemctl disable ModemManager.service systemctl stop ModemManager.service apt-get purge modemmanager # mkdir -p /mnt/usb-stick echo "UUID="52ff610a-2612-4021-8a8d-b818b3dba1f4" /mnt/usb-stick ext4 defaults 0 1" >> /etc/fstab systemctl daemon-reload mount -a
GPIO für USV
aptitude install raspi-gpio # konfiguriere GPIO #18 als Input mit internem Pull-Down: raspi-gpio set 18 ip pd # GPIO Zustand abfragen: raspi-gpio get 18
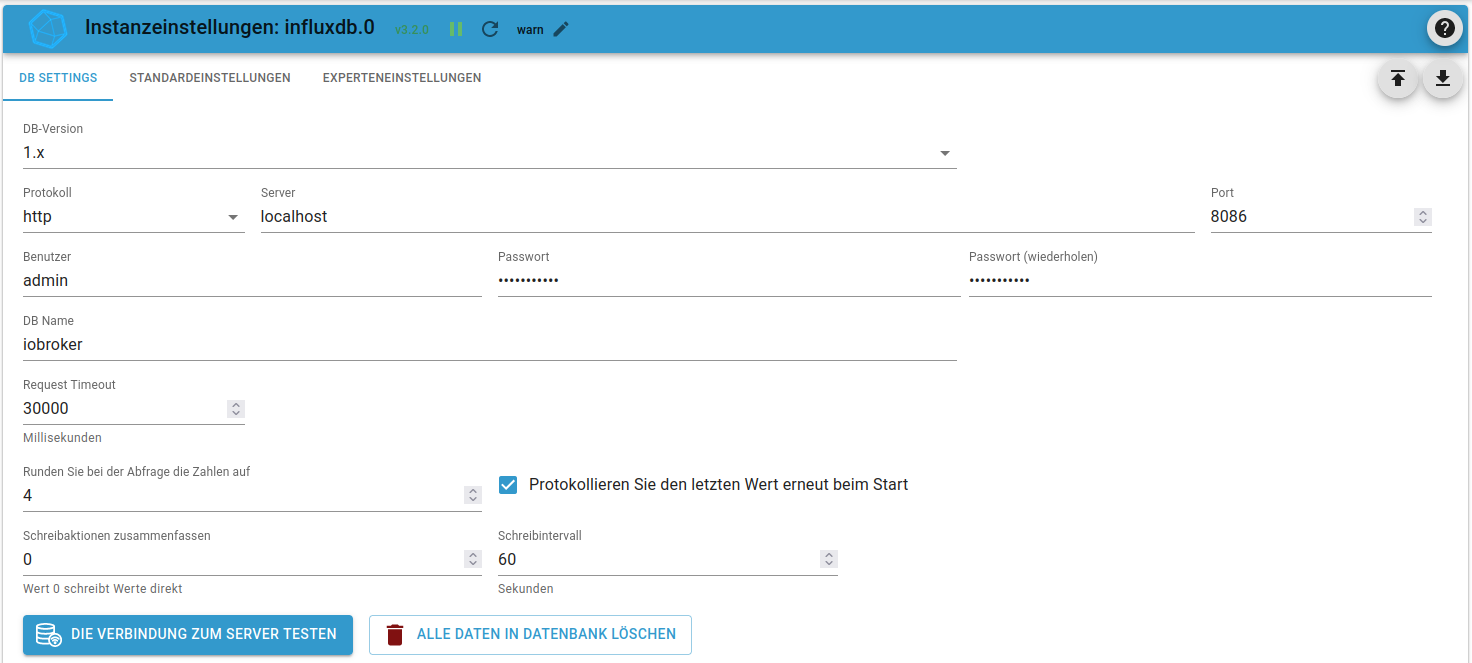
InfluxDB 1.x
Installation
sudo su #wget -qO- https://repos.influxdata.com/influxdata-archive_compat.key | sudo apt-key add - #source /etc/lsb-release #echo "deb https://repos.influxdata.com/${DISTRIB_ID,,} ${DISTRIB_CODENAME} stable" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/influxdb.list #curl https://repos.influxdata.com/influxdata-archive.key | gpg --dearmor | sudo tee /usr/share/keyrings/influxdb-archive-keyring.gpg >/dev/null #echo "deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/influxdb-archive-keyring.gpg] https://repos.influxdata.com/debian $(lsb_release -cs) stable" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/influxdb.list wget -q https://repos.influxdata.com/influxdata-archive_compat.key echo '393e8779c89ac8d958f81f942f9ad7fb82a25e133faddaf92e15b16e6ac9ce4c influxdata-archive_compat.key' | sha256sum -c && cat influxdata-archive_compat.key | gpg --dearmor | sudo tee /etc/apt/trusted.gpg.d/influxdata-archive_compat.gpg > /dev/null echo 'deb [signed-by=/etc/apt/trusted.gpg.d/influxdata-archive_compat.gpg] https://repos.influxdata.com/debian stable main' | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/influxdata.list apt-get update apt-get install influxdb systemctl unmask influxdb.service systemctl enable influxdb systemctl start influxdb systemctl status influxdb
Konfiguration
sudo su influx > CREATE USER "admin" WITH PASSWORD 'influxdbadmin' WITH ALL PRIVILEGES > CREATE USER "iobroker" WITH PASSWORD 'iobroker' > CREATE DATABASE "iobroker" > GRANT ALL ON "iobroker" TO "iobroker" > exit # mcedit /etc/influxdb/influxdb.conf [http] enabled = true bind-address = ":8086" auth-enabled = true log-enabled = true write-tracing = false pprof-enabled = true https-enabled = false # systemctl restart influxdb
Datenbankgröße ermitteln
sudo su du -sh /var/lib/influxdb/data/iobrokerdb/
Backups
Quelle: https://docs.influxdata.com/influxdb/v1/administration/backup_and_restore/#back-up-all-databases
Erstellen
sudo su influxd backup -portable /path/to/backup-destination # or do it in one line: cd /; influxd backup -portable /mnt/usb-stick/backup/influxdb/`date +%Y%m%d`
Wiederherstellen
sudo su influxd restore -portable /path/to/backup-destination
InfluxDB 2.x
Installation
sudo su cd ~ wget -q https://repos.influxdata.com/influxdata-archive_compat.key echo '393e8779c89ac8d958f81f942f9ad7fb82a25e133faddaf92e15b16e6ac9ce4c influxdata-archive_compat.key' | sha256sum -c && cat influxdata-archive_compat.key | gpg --dearmor | sudo tee /etc/apt/trusted.gpg.d/influxdata-archive_compat.gpg > /dev/null echo 'deb [signed-by=/etc/apt/trusted.gpg.d/influxdata-archive_compat.gpg] https://repos.influxdata.com/debian stable main' | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/influxdata.list apt-get update apt-get install influxdb2 systemctl start influxdb systemctl status influxdb
Konfiguration
Die Konfiguration der InfluxDB erfolgt über den Browser via http://RASPI-IP:8086.
Grafana
Installation
sudo su #wget -q -O /usr/share/keyrings/grafana.key https://apt.grafana.com/gpg.key #echo "deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/grafana.key] https://apt.grafana.com stable main" | sudo tee -a /etc/apt/sources.list.d/grafana.list wget -q -O - https://packages.grafana.com/gpg.key | sudo apt-key add - echo "deb https://packages.grafana.com/oss/deb stable main" | sudo tee -a /etc/apt/sources.list.d/grafana.list apt-get update # Install the latest OSS release: apt-get install -y grafana # Start System Service aka. Server systemctl daemon-reload systemctl start grafana-server systemctl status grafana-server systemctl enable grafana-server.service
Grafana Server: http://IP:3000
Grafana ohne Login
mcedit /etc/grafana/grafana.ini # [auth.anonymous] enabled = true systemctl restart grafana-server
Backup
Erstellen
sudo su cp /var/lib/grafana/grafana.db /path/to/backup-destination cp /etc/grafana/grafana.ini /path/to/backup-destination # or do it in one line: cd /; mkdir /mnt/usb-stick/backup/grafana/`date +%Y%m%d`; cp /etc/grafana/grafana.ini /mnt/usb-stick/backup/grafana/`date +%Y%m%d`; cp /var/lib/grafana/grafana.db /mnt/usb-stick/backup/grafana/`date +%Y%m%d`
Wiederherstellen
sudo su cd /path/to/backup-destination cp grafana.db /var/lib/grafana/ cp grafana.ini /etc/grafana/
ioBroker
Wiederherstellung
Folgende Backup Dateien via Backitup Adapter wieder einsoielen:
- iobroker_<TIMESTAMP>_backupiobroker.tar.gz
- influxDB_<TIMESTAMP>_backupiobroker.tar.gz
- grafana_<TIMESTAMP>_backupiobroker.tar.gz
- javascripts_<TIMESTAMP>_backupiobroker.tar.gz
Installation
sudo su # automatische Installation: curl -sLf https://iobroker.net/install.sh | bash -
Nach der Installation ist die ioBroker Instanz erreichbar unter http://<Raspberry-Pi-IP>:8081.
Steuerung
# ioBroker starten: iobroker start # ioBroker stoppen: iobroker stop # ioBrker Infos anzeigen iobroker info
Backups
Erstellung
Siehe unten → Script oder per 'Backitup' Adapter
Wiederherstellung
- Verzeichniss '/opt/iobroker/backups' anlegen
- Kopieren des Backups dort hinein
Backups die mit dem Backitup-Adapter erstellt wurden können nachde dem kopieren via Web-Interface wieder eingesielt werden.
Alternativ kann auch die Konsole verwendet werden:
sudo su cd /opt/iobroker iobroker stop iobroker restore 0 iobroker stop
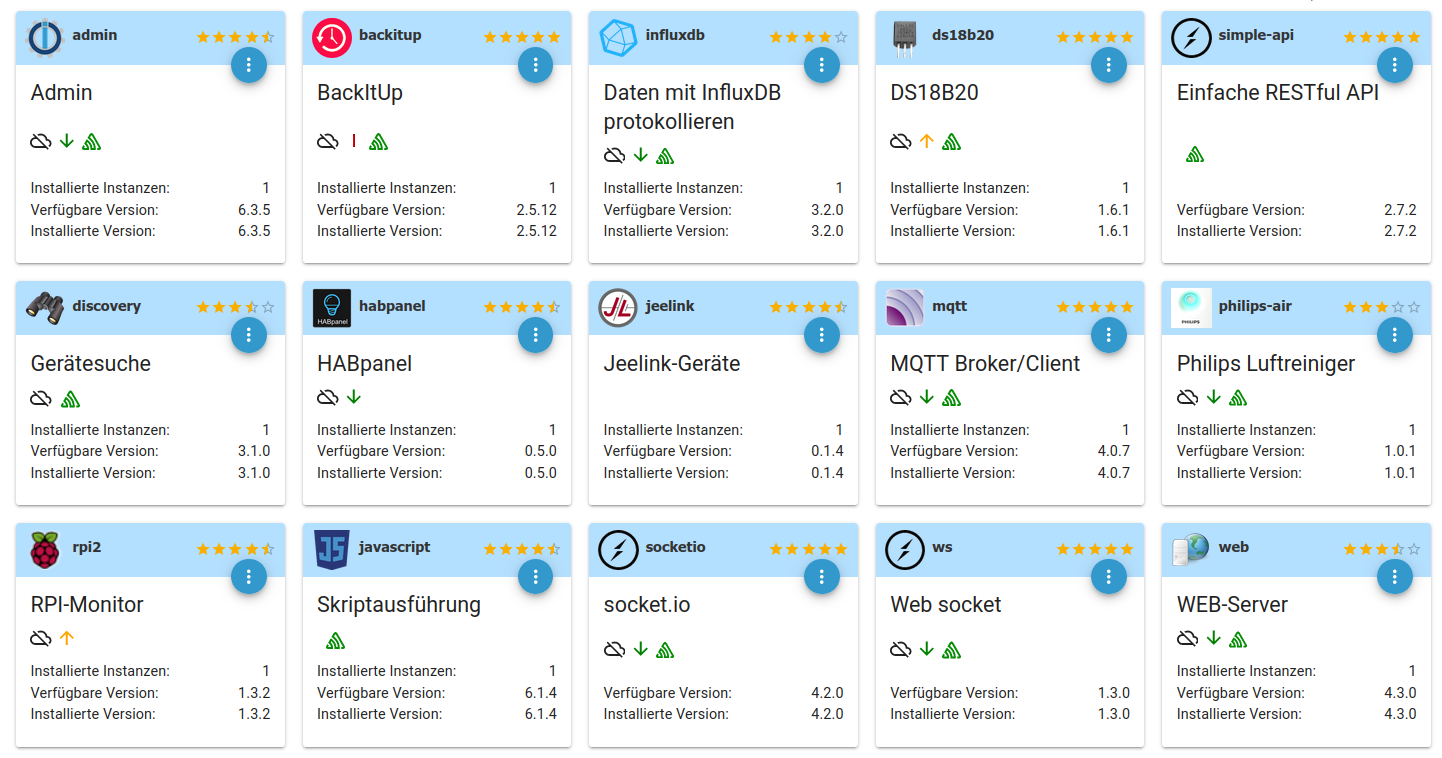
Adapter installieren
Als Adapter werden alle Schnittstellen zu externen aber auch zu internen Datenquellen (z.B. Shelly Sensoren, Temperatur, Luftfeuchte, GPIO, 1-Wire, etc.) und Senken (Shelly Aktoren) bezeichnet.
- influxDB (Datenbank zur Speicherung von Messwerten)
- DS18B20 (Auslesen von 1-Wire Temperatursensoren)
- HABpanel (Steuerung von Aktoren vis Webseite)
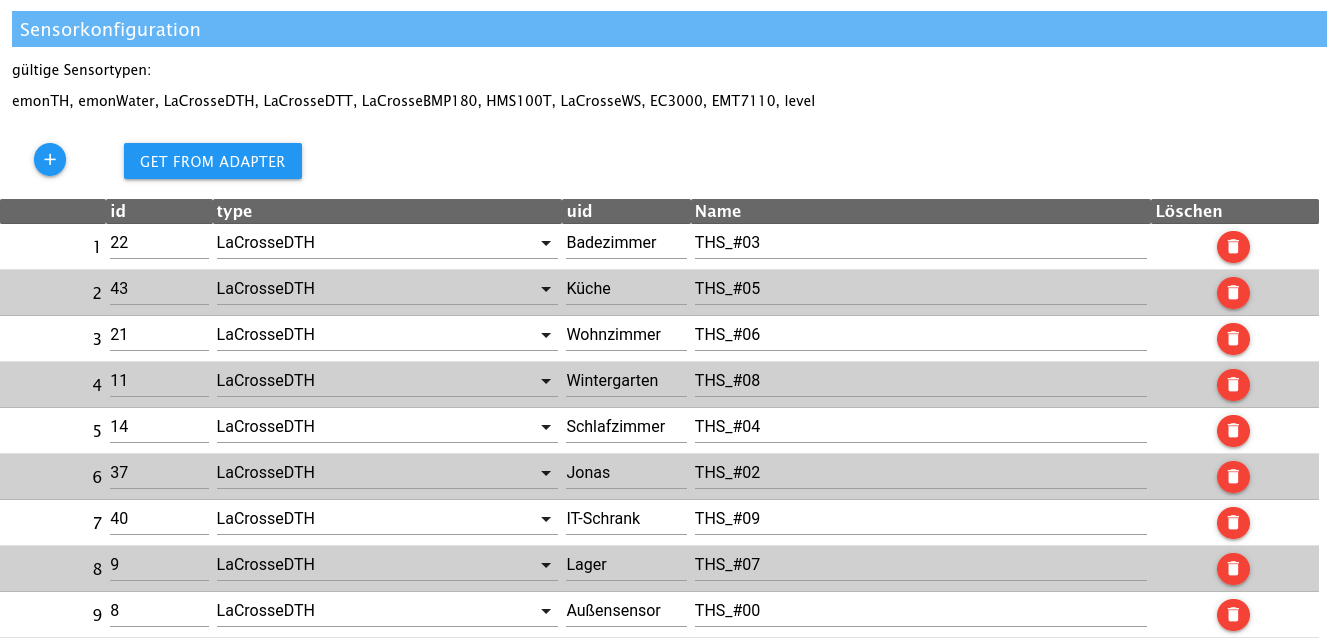
- Jeelink-Geräte (Empfangen von 868mHz LaCrosse Temperatur- und Feuchtesensoren (hier z.B. TX29DTH-IT) mit Hilfe eines Jeelink Klones
- MQTT Broker (zur Datenverarbeitung von MQTT-fähigen Sensoren und Aktoren)
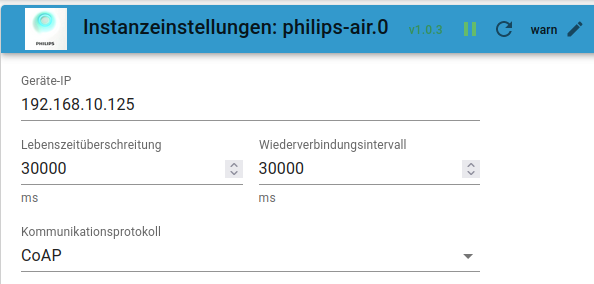
- Philips Luftreiniger (für die Anbindung eines Philips Air Purifier 4000i Series (Typ: AC4236/10)
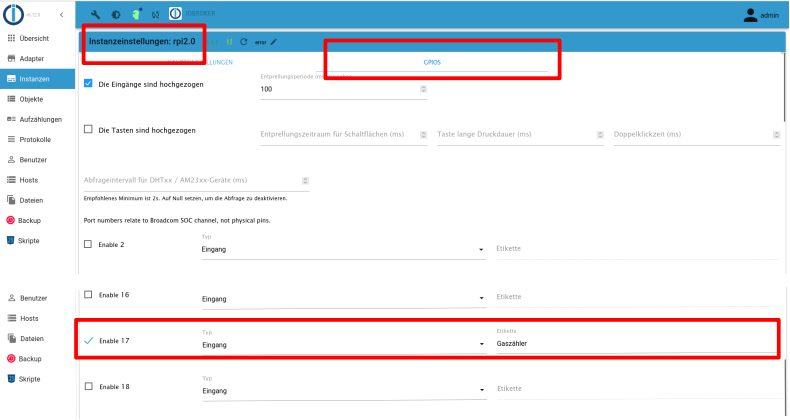
- RPI-Monitor (Nutzung von GPIOs z.B. zum Einlesen eines Reed-Kontaktes für den Gaszähler)
- Skriptausführung (Javascript und Blockly)
- WEB-Server (für HABpanel)
- Shelly
Adapter konfigurieren
Die oben aufgeführten Adapter sind nach der Installation unter Instanzen zu finden und müssen dort konfiguriert werden.
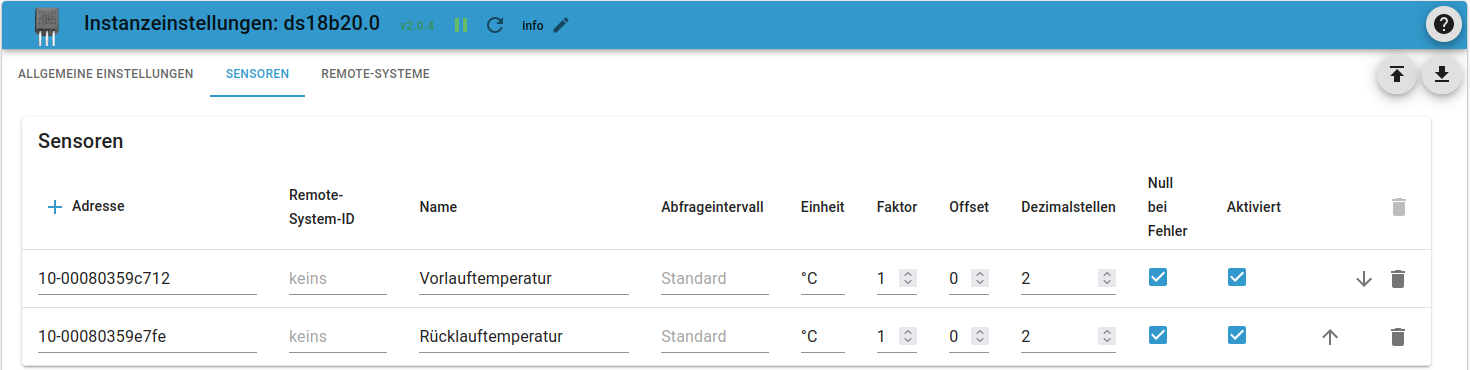
1-Wire
DS18B20
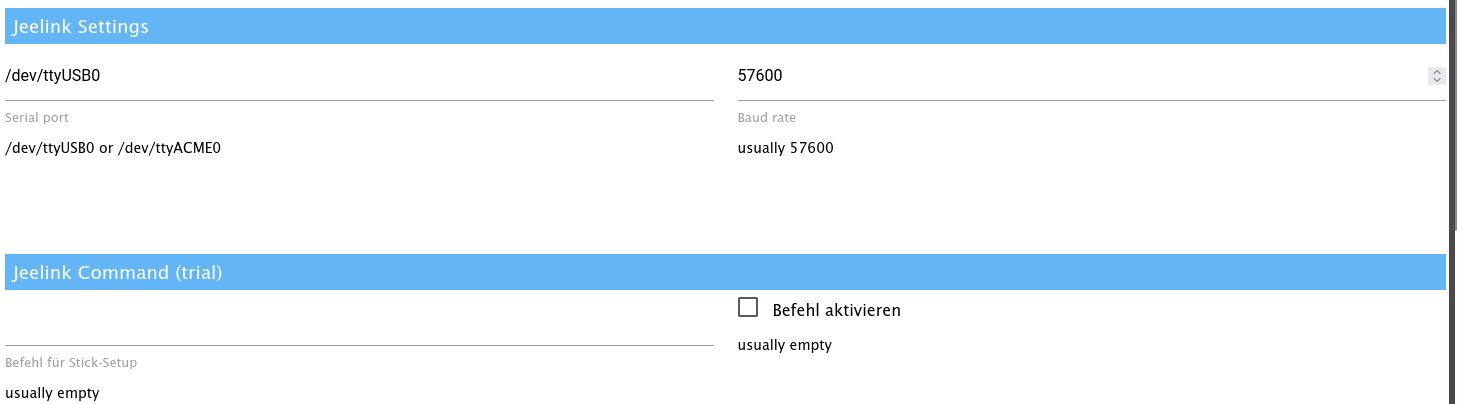
JeeLink
MQTT
Für IKEA Sensoren –> Die angepasste Firmware gibt es hier.
Philips
Gaszähler
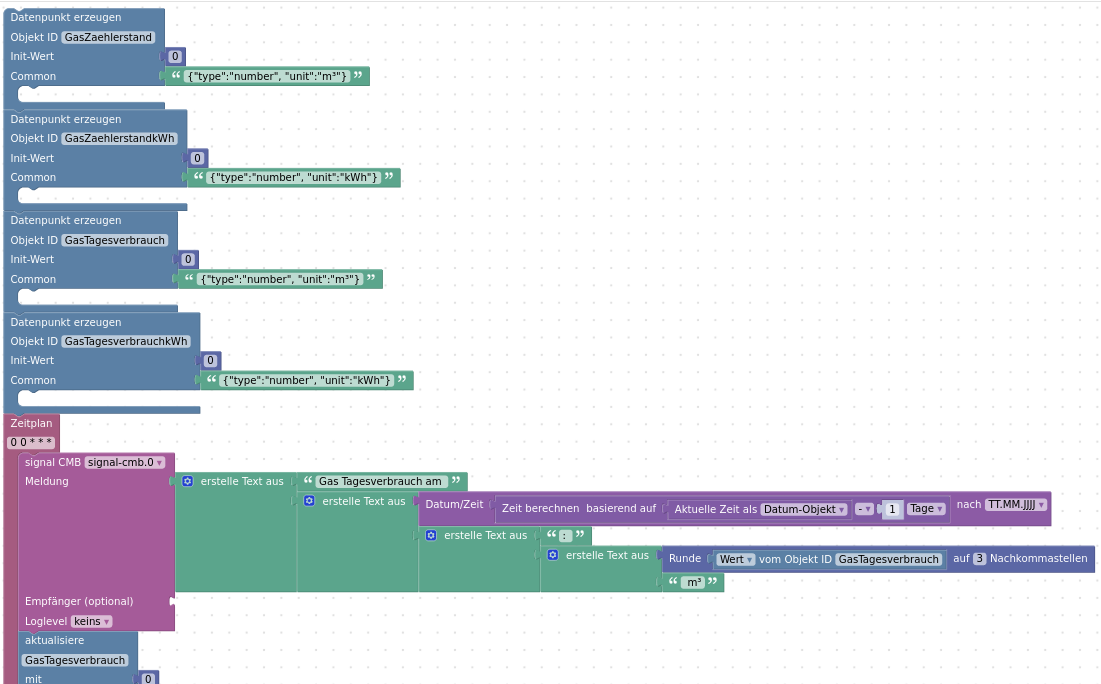
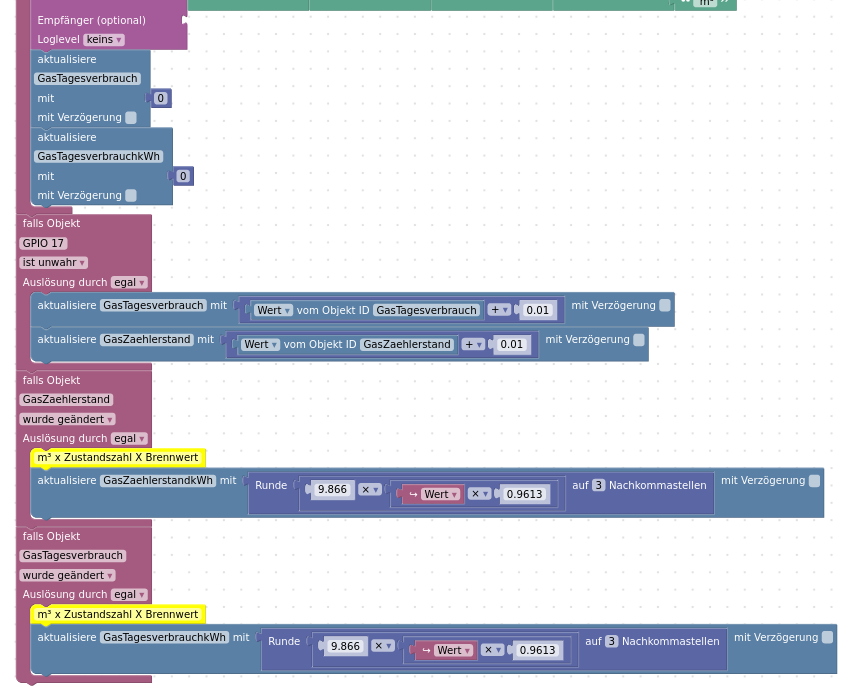
Blockly
Und das ganze als XML:
++++ Title |
- gaszaehler_blockly.xml
<xml xmlns="https://developers.google.com/blockly/xml"> <block type="create" id="0B{}LlRd,d!Br67@Vlbv" x="113" y="-112"> <field name="NAME">GasZaehlerstand</field> <value name="VALUE"> <block type="math_number" id="zCMHZ;$=evsZ~g#$%B,d"> <field name="NUM">0</field> </block> </value> <value name="COMMON"> <block type="text" id="+waJXiBe~1dn@SNBXD]b"> <field name="TEXT">{"type":"number", "unit":"m³"}</field> </block> </value> <next> <block type="create" id="2[=]D*fweUy]z]fKRb*N"> <field name="NAME">GasZaehlerstandkWh</field> <value name="VALUE"> <block type="math_number" id="6#vjQv4JhiY|mZ`tva4+"> <field name="NUM">0</field> </block> </value> <value name="COMMON"> <block type="text" id="lD}p7.V%=!S:e/(Pj1[e"> <field name="TEXT">{"type":"number", "unit":"kWh"}</field> </block> </value> <next> <block type="create" id="Jt^U$w~,3R~)UPJJP+$c"> <field name="NAME">GasTagesverbrauch</field> <value name="VALUE"> <block type="math_number" id="ob;_09!^uke_;c@UqtCZ"> <field name="NUM">0</field> </block> </value> <value name="COMMON"> <block type="text" id="Br7y=,dGAF9I]mb?z-,:"> <field name="TEXT">{"type":"number", "unit":"m³"}</field> </block> </value> <next> <block type="create" id="0S(2ltH~c|{]uV)aZEoI"> <field name="NAME">GasTagesverbrauchkWh</field> <value name="VALUE"> <block type="math_number" id="uL]uOd@Q!FgAK,u/~1i0"> <field name="NUM">0</field> </block> </value> <value name="COMMON"> <block type="text" id="?PxPe$PT.{E1el.m,Fl{"> <field name="TEXT">{"type":"number", "unit":"kWh"}</field> </block> </value> <next> <block type="schedule" id="#TX=ZX{-w2cu=Uj!nuO*"> <field name="SCHEDULE">0 0 * * *</field> <statement name="STATEMENT"> <block type="signal-cmb" id="n4NEdLb^*N-$c[YJUMw_"> <field name="INSTANCE">.0</field> <field name="LOG"></field> <value name="MESSAGE"> <shadow type="text" id="F/ePx6FSOr+[BT|hOL68"> <field name="TEXT">text</field> </shadow> <block type="text_join" id="+A!rZ(7aVj!~E{6~WV0m"> <mutation items="2"></mutation> <value name="ADD0"> <block type="text" id="8EJ*o[R;:^=5;).KbZeh"> <field name="TEXT">Gas Tagesverbrauch am </field> </block> </value> <value name="ADD1"> <block type="text_join" id="HeWwloE2zR[^)91A5vLf"> <mutation items="2"></mutation> <value name="ADD0"> <block type="convert_from_date" id="s;*kY*B;HuSZ^~w0=Q1B"> <mutation xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" format="false" language="false"></mutation> <field name="OPTION">DD.MM.YYYY</field> <value name="VALUE"> <block type="time_calculation" id="YM!lstPQJsLk~Nr|/C9S"> <field name="OPERATION">-</field> <field name="UNIT">day</field> <value name="DATE_TIME"> <shadow type="time_get" id="*vxqb!BXG7I/C$mm0(,6"> <mutation xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" format="false" language="false"></mutation> <field name="OPTION">object</field> </shadow> <block type="time_get" id="c7c*a4_Wl/:1^bYj[5Gv"> <mutation xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" format="false" language="false"></mutation> <field name="OPTION">object</field> </block> </value> <value name="VALUE"> <shadow type="math_number" id="|4-%[@-^:5+J56T:106m"> <field name="NUM">1</field> </shadow> </value> </block> </value> </block> </value> <value name="ADD1"> <block type="text_join" id="=%;,#+%QHjmLt3hl!=~r"> <mutation items="2"></mutation> <value name="ADD0"> <block type="text" id="3:2kP58oTBRcZi2),~ld"> <field name="TEXT">: </field> </block> </value> <value name="ADD1"> <block type="text_join" id="tmVWY7$h@F7sTbDx8RxC"> <mutation items="2"></mutation> <value name="ADD0"> <block type="math_rndfixed" id="r$r$dA.ncKJ|_gq606gB"> <field name="n">3</field> <value name="x"> <shadow type="math_number" id="AThWyAlfX]`^N:24Bj)1"> <field name="NUM">3.1234</field> </shadow> <block type="get_value" id="#R/Z*/!V{2!I`w97g5#$"> <field name="ATTR">val</field> <field name="OID">javascript.0.GasTagesverbrauch</field> </block> </value> </block> </value> <value name="ADD1"> <block type="text" id="wPYk)Zw6;xd5M2HRI[=?"> <field name="TEXT"> m³</field> </block> </value> </block> </value> </block> </value> </block> </value> </block> </value> <next> <block type="update" id="@0uFnK3p@d(aFNzT|/lb" inline="false"> <mutation xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" delay_input="false"></mutation> <field name="OID">javascript.0.GasTagesverbrauch</field> <field name="WITH_DELAY">FALSE</field> <value name="VALUE"> <block type="math_number" id="4)r,X`Fg.[q=u_H*lfRk"> <field name="NUM">0</field> </block> </value> <next> <block type="update" id="TI_1t%q+ZcJ4QYR55c_V" inline="false"> <mutation xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" delay_input="false"></mutation> <field name="OID">javascript.0.GasTagesverbrauchkWh</field> <field name="WITH_DELAY">FALSE</field> <value name="VALUE"> <block type="math_number" id="r%v}PcT3aL`Ou#bfv}2v"> <field name="NUM">0</field> </block> </value> </block> </next> </block> </next> </block> </statement> <next> <block type="on" id="4Y-zykZ$Wh;oiRmsNJ5@"> <field name="OID">rpi2.0.gpio.17.state</field> <field name="CONDITION">false</field> <field name="ACK_CONDITION"></field> <statement name="STATEMENT"> <block type="update" id="9]|sNN!RG]pSo)u[+a:l"> <mutation xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" delay_input="false"></mutation> <field name="OID">javascript.0.GasTagesverbrauch</field> <field name="WITH_DELAY">FALSE</field> <value name="VALUE"> <block type="math_arithmetic" id="6}2q8C;`zJ=g7E_fxS}|"> <field name="OP">ADD</field> <value name="A"> <shadow type="math_number" id="bh@Wx=0!@N|v#@:zwozA"> <field name="NUM">1</field> </shadow> <block type="get_value" id="kR$.7#of[Q%v[4%`)`qw"> <field name="ATTR">val</field> <field name="OID">javascript.0.GasTagesverbrauch</field> </block> </value> <value name="B"> <shadow type="math_number" id="U_G`SdC1Ek1LOeD^e0GZ"> <field name="NUM">0.01</field> </shadow> </value> </block> </value> <next> <block type="update" id="KH(0kBhtIn0cIneAPNH$"> <mutation xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" delay_input="false"></mutation> <field name="OID">javascript.0.GasZaehlerstand</field> <field name="WITH_DELAY">FALSE</field> <value name="VALUE"> <block type="math_arithmetic" id="JllB@rBhaoQ78i!%QiN@"> <field name="OP">ADD</field> <value name="A"> <shadow type="math_number" id="bh@Wx=0!@N|v#@:zwozA"> <field name="NUM">1</field> </shadow> <block type="get_value" id=";Rlcv?|LRTX~#Ib;c81n"> <field name="ATTR">val</field> <field name="OID">javascript.0.GasZaehlerstand</field> </block> </value> <value name="B"> <shadow type="math_number" id="vl8GbhNo/:J]~V5.2V5z"> <field name="NUM">0.01</field> </shadow> </value> </block> </value> </block> </next> </block> </statement> <next> <block type="on" id="X7m/%;,l,u[1#P61eH}b"> <field name="OID">javascript.0.GasZaehlerstand</field> <field name="CONDITION">ne</field> <field name="ACK_CONDITION"></field> <statement name="STATEMENT"> <block type="comment" id="[Q_/w^nv`)y#;e4ru1nD"> <field name="COMMENT">m³ x Zustandszahl X Brennwert</field> <next> <block type="update" id="8.z/}1(PYiq*8X7[Q9Ae"> <mutation xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" delay_input="false"></mutation> <field name="OID">javascript.0.GasZaehlerstandkWh</field> <field name="WITH_DELAY">FALSE</field> <value name="VALUE"> <block type="math_rndfixed" id="+O$=HuhMm)nj7_OOc56="> <field name="n">3</field> <value name="x"> <shadow type="math_number" id="aeqHXH7yQcf5k2Qn,tC/"> <field name="NUM">3.1234</field> </shadow> <block type="math_arithmetic" id="(N6Ay,~*P)f+G|I0~!p2"> <field name="OP">MULTIPLY</field> <value name="A"> <shadow type="math_number" id="XwM0.cfS~dYqK@(o/Pc)"> <field name="NUM">9.866</field> </shadow> </value> <value name="B"> <shadow type="math_number" id="}/IuLzLcCeHe!b~b/VO~"> <field name="NUM">1</field> </shadow> <block type="math_arithmetic" id="7w-+v.aROeGiRwfMHXNM"> <field name="OP">MULTIPLY</field> <value name="A"> <shadow type="math_number" id="%qWr/Hv}vgETQg]nGDE9"> <field name="NUM">1</field> </shadow> <block type="on_source" id="KxNJKuqKY/]s[I!V$Mol"> <field name="ATTR">state.val</field> </block> </value> <value name="B"> <shadow type="math_number" id="M}_|BoUHL8urPnuw;e9="> <field name="NUM">0.9613</field> </shadow> </value> </block> </value> </block> </value> </block> </value> </block> </next> </block> </statement> <next> <block type="on" id="1,.5mB=(/f/jzm?Qa)50"> <field name="OID">javascript.0.GasTagesverbrauch</field> <field name="CONDITION">ne</field> <field name="ACK_CONDITION"></field> <statement name="STATEMENT"> <block type="comment" id="-m![Gh^zQ_@npOAF3~!!"> <field name="COMMENT">m³ x Zustandszahl X Brennwert</field> <next> <block type="update" id="8:U}a~4U+pX]:KTxvyW}"> <mutation xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" delay_input="false"></mutation> <field name="OID">javascript.0.GasTagesverbrauchkWh</field> <field name="WITH_DELAY">FALSE</field> <value name="VALUE"> <block type="math_rndfixed" id="YcCf+;GbSY/PZ.e(zMeH"> <field name="n">3</field> <value name="x"> <shadow type="math_number" id="aeqHXH7yQcf5k2Qn,tC/"> <field name="NUM">3.1234</field> </shadow> <block type="math_arithmetic" id="%.k-kW,6s)i$)dOkK2[Y"> <field name="OP">MULTIPLY</field> <value name="A"> <shadow type="math_number" id="R^,D.8GKv}Jv!N-k5,?w"> <field name="NUM">9.866</field> </shadow> </value> <value name="B"> <shadow type="math_number" id="}/IuLzLcCeHe!b~b/VO~"> <field name="NUM">1</field> </shadow> <block type="math_arithmetic" id="GZh_TDV2T-Wfkl$v.6%B"> <field name="OP">MULTIPLY</field> <value name="A"> <shadow type="math_number" id="%qWr/Hv}vgETQg]nGDE9"> <field name="NUM">1</field> </shadow> <block type="on_source" id="j6OtdQ-opx@n@HuS.5;["> <field name="ATTR">state.val</field> </block> </value> <value name="B"> <shadow type="math_number" id="w[4vjUZR~ib${TrBsYgL"> <field name="NUM">0.9613</field> </shadow> </value> </block> </value> </block> </value> </block> </value> </block> </next> </block> </statement> </block> </next> </block> </next> </block> </next> </block> </next> </block> </next> </block> </next> </block> </next> </block> </xml>
++++
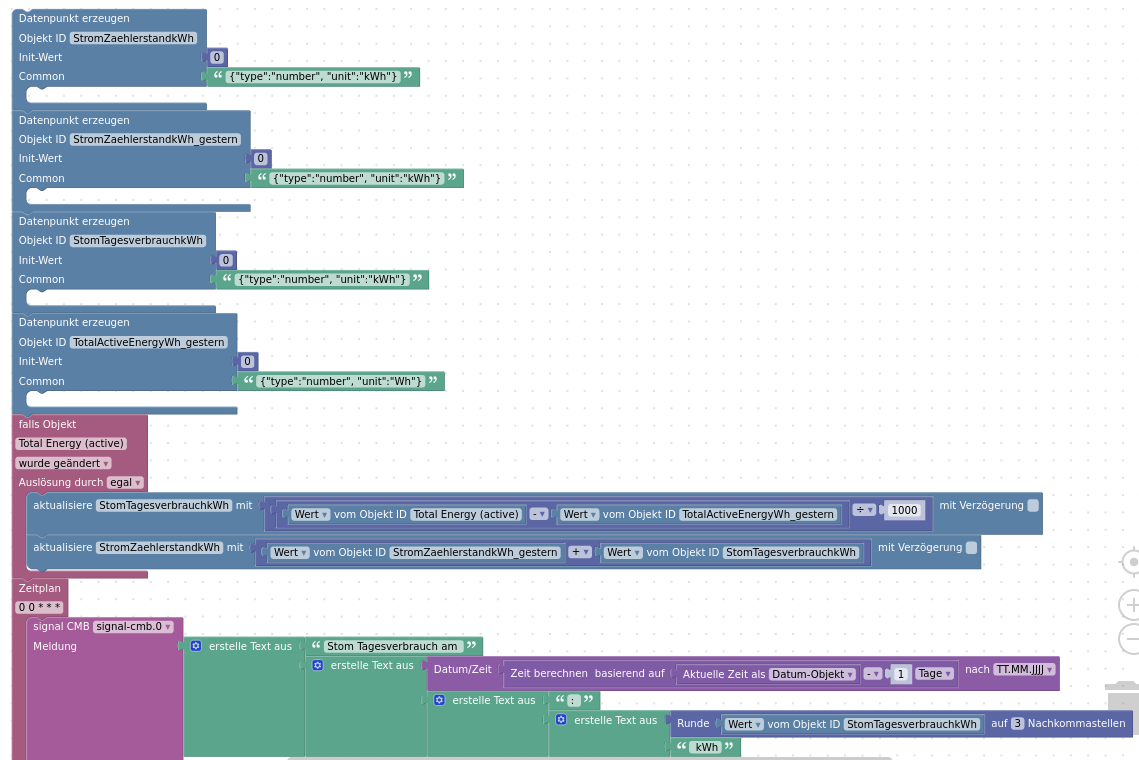
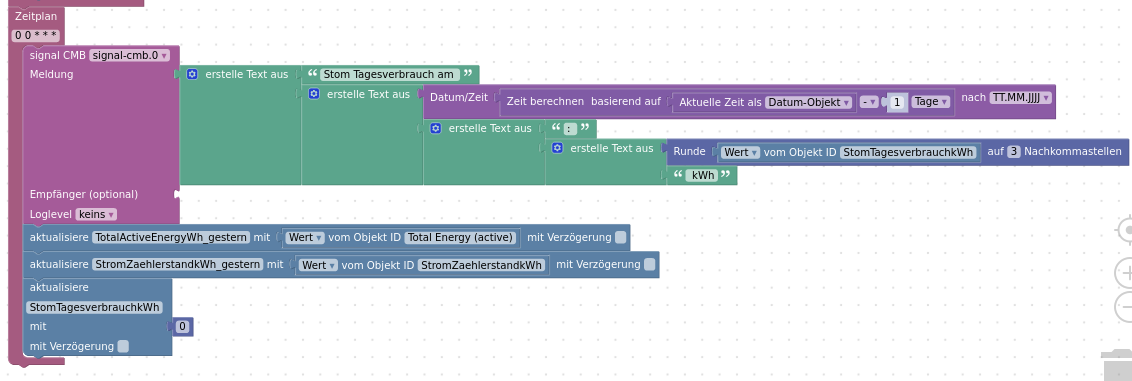
Stromzähler
Zur Erfassung des Stromverbrauches meiner Wohnung verwende ich einen Shelly 3EM Pro den ich via Shelly Adapter eingebunden habe.
Blockly
Und das ganze als XML:
++++ Title |
- strozaehler_blockly.xml
<xml xmlns="https://developers.google.com/blockly/xml"> <block type="create" id="WNiKV(pYZ3,|L9mDGTHD" x="138" y="-62"> <field name="NAME">StromZaehlerstandkWh</field> <value name="VALUE"> <block type="math_number" id="0F`c7%Isi~b|@epORR*S"> <field name="NUM">0</field> </block> </value> <value name="COMMON"> <block type="text" id="/1(k)OA[2kB~j;PxbH_4"> <field name="TEXT">{"type":"number", "unit":"kWh"}</field> </block> </value> <next> <block type="create" id="2[=]D*fweUy]z]fKRb*N"> <field name="NAME">StromZaehlerstandkWh_gestern</field> <value name="VALUE"> <block type="math_number" id="6#vjQv4JhiY|mZ`tva4+"> <field name="NUM">0</field> </block> </value> <value name="COMMON"> <block type="text" id="lD}p7.V%=!S:e/(Pj1[e"> <field name="TEXT">{"type":"number", "unit":"kWh"}</field> </block> </value> <next> <block type="create" id="0S(2ltH~c|{]uV)aZEoI"> <field name="NAME">StomTagesverbrauchkWh</field> <value name="VALUE"> <block type="math_number" id="uL]uOd@Q!FgAK,u/~1i0"> <field name="NUM">0</field> </block> </value> <value name="COMMON"> <block type="text" id="?PxPe$PT.{E1el.m,Fl{"> <field name="TEXT">{"type":"number", "unit":"kWh"}</field> </block> </value> <next> <block type="create" id="rss(Q.udF1BQD5Bz@T7~"> <field name="NAME">TotalActiveEnergyWh_gestern</field> <value name="VALUE"> <block type="math_number" id="tx?^zyUsJqm}GHq-b.f3"> <field name="NUM">0</field> </block> </value> <value name="COMMON"> <block type="text" id="xDII{fs[B3khS-DSylb8"> <field name="TEXT">{"type":"number", "unit":"Wh"}</field> </block> </value> <next> <block type="on" id="?c^{.iN$6fj256L#A8Ql"> <field name="OID">shelly.0.shellypro3em#c8f09e8314fc#1.EMData0.TotalActiveEnergy</field> <field name="CONDITION">ne</field> <field name="ACK_CONDITION"></field> <statement name="STATEMENT"> <block type="update" id="g+V`|DyKF[}Pmy=+sl;O"> <mutation xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" delay_input="false"></mutation> <field name="OID">javascript.0.StomTagesverbrauchkWh</field> <field name="WITH_DELAY">FALSE</field> <value name="VALUE"> <block type="math_arithmetic" id="11dXVHhW_NGn{g;5pw_+"> <field name="OP">DIVIDE</field> <value name="A"> <shadow type="math_number" id="v-*1r6*(O74YeD/hDb~_"> <field name="NUM">1</field> </shadow> <block type="math_arithmetic" id=";nKGmG#8.~l5jQA,gp[o"> <field name="OP">MINUS</field> <value name="A"> <shadow type="math_number" id="@8B(O2U-tIrBZ2qRS*QM"> <field name="NUM">1</field> </shadow> <block type="get_value" id="]jZ_e/iQou/O4%E2EUcM"> <field name="ATTR">val</field> <field name="OID">shelly.0.shellypro3em#c8f09e8314fc#1.EMData0.TotalActiveEnergy</field> </block> </value> <value name="B"> <shadow type="math_number" id="b6Bt(ksp=pv)Rge1D{;r"> <field name="NUM">1</field> </shadow> <block type="get_value" id="l+nL:/(/S=]UY|M2-#7M"> <field name="ATTR">val</field> <field name="OID">javascript.0.TotalActiveEnergyWh_gestern</field> </block> </value> </block> </value> <value name="B"> <shadow type="math_number" id="nkI`PVg;I,we%ojJ,TA*"> <field name="NUM">1000</field> </shadow> </value> </block> </value> <next> <block type="update" id="SJs~Ys@X?5pv50XP=wqj"> <mutation xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" delay_input="false"></mutation> <field name="OID">javascript.0.StromZaehlerstandkWh</field> <field name="WITH_DELAY">FALSE</field> <value name="VALUE"> <block type="math_arithmetic" id="},ExWVJxj)o(5=vmy1.e"> <field name="OP">ADD</field> <value name="A"> <shadow type="math_number" id="@8B(O2U-tIrBZ2qRS*QM"> <field name="NUM">1</field> </shadow> <block type="get_value" id="_#ZSu=g6=)eF7:(ey4Bh"> <field name="ATTR">val</field> <field name="OID">javascript.0.StromZaehlerstandkWh_gestern</field> </block> </value> <value name="B"> <shadow type="math_number" id="H-iY+5=={P}IKvpkKUi;"> <field name="NUM">1</field> </shadow> <block type="get_value" id="?DIb~Cgt]yKCn?Eau4?j"> <field name="ATTR">val</field> <field name="OID">javascript.0.StomTagesverbrauchkWh</field> </block> </value> </block> </value> </block> </next> </block> </statement> <next> <block type="schedule" id="#TX=ZX{-w2cu=Uj!nuO*"> <field name="SCHEDULE">0 0 * * *</field> <statement name="STATEMENT"> <block type="signal-cmb" id="n4NEdLb^*N-$c[YJUMw_"> <field name="INSTANCE">.0</field> <field name="LOG"></field> <value name="MESSAGE"> <shadow type="text" id="F/ePx6FSOr+[BT|hOL68"> <field name="TEXT">text</field> </shadow> <block type="text_join" id="+A!rZ(7aVj!~E{6~WV0m"> <mutation items="2"></mutation> <value name="ADD0"> <block type="text" id="8EJ*o[R;:^=5;).KbZeh"> <field name="TEXT">Stom Tagesverbrauch am </field> </block> </value> <value name="ADD1"> <block type="text_join" id="HeWwloE2zR[^)91A5vLf"> <mutation items="2"></mutation> <value name="ADD0"> <block type="convert_from_date" id="s;*kY*B;HuSZ^~w0=Q1B"> <mutation xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" format="false" language="false"></mutation> <field name="OPTION">DD.MM.YYYY</field> <value name="VALUE"> <block type="time_calculation" id="YM!lstPQJsLk~Nr|/C9S"> <field name="OPERATION">-</field> <field name="UNIT">day</field> <value name="DATE_TIME"> <shadow type="time_get" id="*vxqb!BXG7I/C$mm0(,6"> <mutation xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" format="false" language="false"></mutation> <field name="OPTION">object</field> </shadow> <block type="time_get" id="c7c*a4_Wl/:1^bYj[5Gv"> <mutation xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" format="false" language="false"></mutation> <field name="OPTION">object</field> </block> </value> <value name="VALUE"> <shadow type="math_number" id="|4-%[@-^:5+J56T:106m"> <field name="NUM">1</field> </shadow> </value> </block> </value> </block> </value> <value name="ADD1"> <block type="text_join" id="=%;,#+%QHjmLt3hl!=~r"> <mutation items="2"></mutation> <value name="ADD0"> <block type="text" id="3:2kP58oTBRcZi2),~ld"> <field name="TEXT">: </field> </block> </value> <value name="ADD1"> <block type="text_join" id="tmVWY7$h@F7sTbDx8RxC"> <mutation items="2"></mutation> <value name="ADD0"> <block type="math_rndfixed" id="r$r$dA.ncKJ|_gq606gB"> <field name="n">3</field> <value name="x"> <shadow type="math_number" id="AThWyAlfX]`^N:24Bj)1"> <field name="NUM">3.1234</field> </shadow> <block type="get_value" id="#R/Z*/!V{2!I`w97g5#$"> <field name="ATTR">val</field> <field name="OID">javascript.0.StomTagesverbrauchkWh</field> </block> </value> </block> </value> <value name="ADD1"> <block type="text" id="wPYk)Zw6;xd5M2HRI[=?"> <field name="TEXT"> kWh</field> </block> </value> </block> </value> </block> </value> </block> </value> </block> </value> <next> <block type="update" id="Ndg}sO%K1?awGPp}[),)"> <mutation xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" delay_input="false"></mutation> <field name="OID">javascript.0.TotalActiveEnergyWh_gestern</field> <field name="WITH_DELAY">FALSE</field> <value name="VALUE"> <block type="get_value" id="8|m`jKyWKA/LP=!E(Xkw"> <field name="ATTR">val</field> <field name="OID">shelly.0.shellypro3em#c8f09e8314fc#1.EMData0.TotalActiveEnergy</field> </block> </value> <next> <block type="update" id="05;QEhX_vzA~$gGS^OQ-"> <mutation xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" delay_input="false"></mutation> <field name="OID">javascript.0.StromZaehlerstandkWh_gestern</field> <field name="WITH_DELAY">FALSE</field> <value name="VALUE"> <block type="get_value" id="Zb6figE|CI],mV=zy!AK"> <field name="ATTR">val</field> <field name="OID">javascript.0.StromZaehlerstandkWh</field> </block> </value> <next> <block type="update" id="@0uFnK3p@d(aFNzT|/lb" inline="false"> <mutation xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" delay_input="false"></mutation> <field name="OID">javascript.0.StomTagesverbrauchkWh</field> <field name="WITH_DELAY">FALSE</field> <value name="VALUE"> <block type="math_number" id="4)r,X`Fg.[q=u_H*lfRk"> <field name="NUM">0</field> </block> </value> </block> </next> </block> </next> </block> </next> </block> </statement> </block> </next> </block> </next> </block> </next> </block> </next> </block> </next> </block> </xml>
++++
InfluxDB
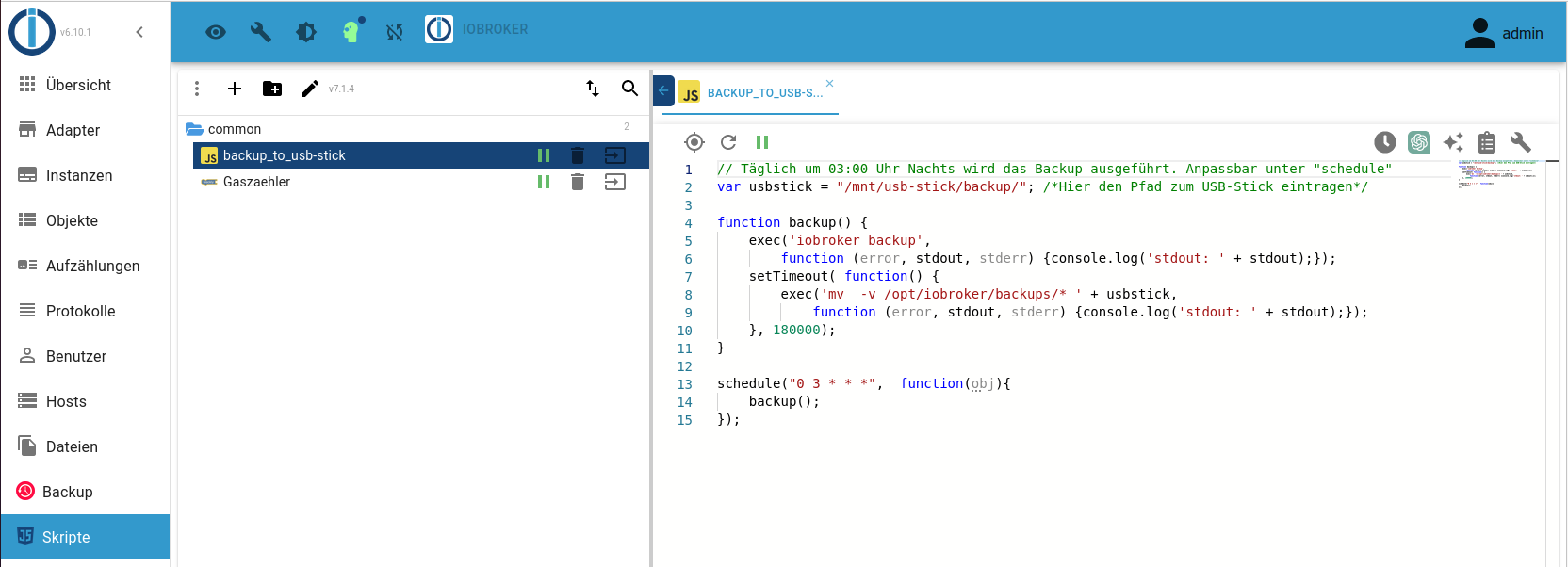
Backup durch Script
// Täglich um 03:00 Uhr Nachts wird das Backup ausgeführt. Anpassbar unter "schedule" var usbstick = "/mnt/usb-stick/backup/"; /*Hier den Pfad zum USB-Stick eintragen*/ function backup() { exec('iobroker backup', function (error, stdout, stderr) {console.log('stdout: ' + stdout);}); setTimeout( function() { exec('mv -v /opt/iobroker/backups/* ' + usbstick, function (error, stdout, stderr) {console.log('stdout: ' + stdout);}); }, 180000); } schedule("0 3 * * *", function(obj){ backup(); });
Update und Bugfixing
iobroker stop
iobroker update
iobroker fix
# oder curl -sL https://iobroker.net/fix.sh | bash -
iobroker upgrade self
iobroker start